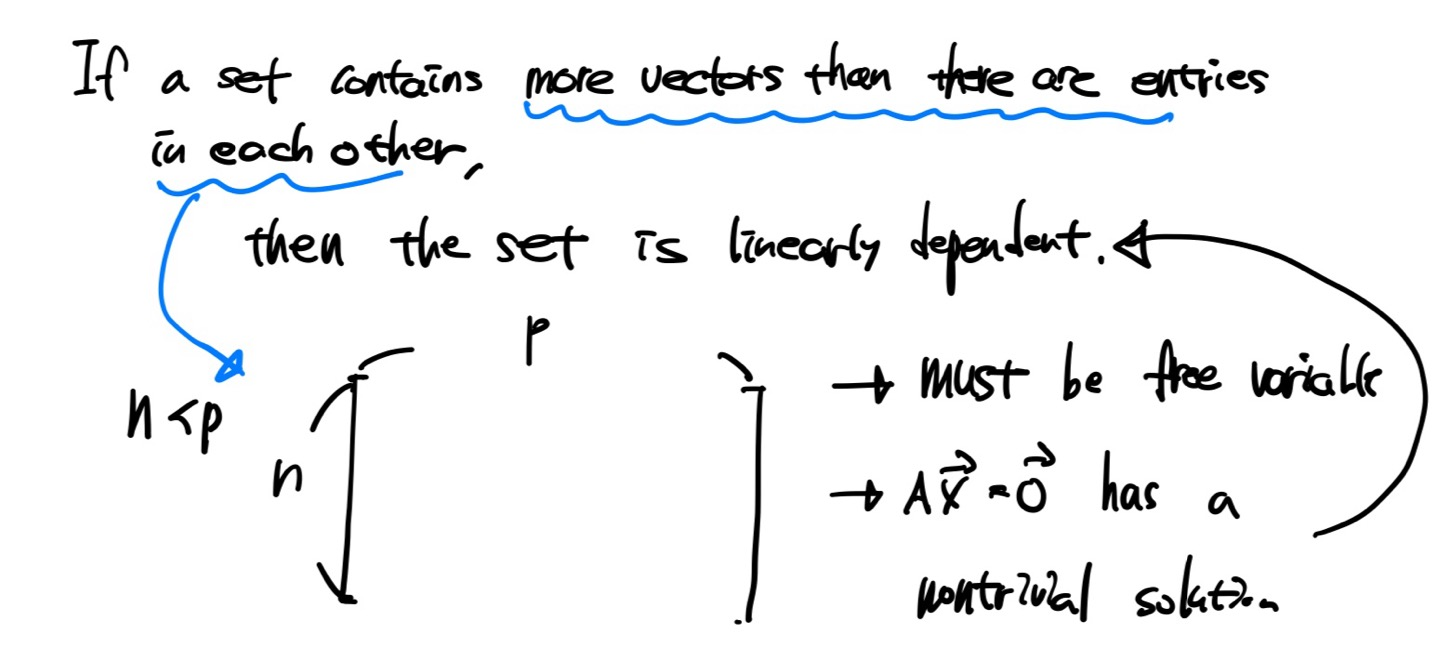
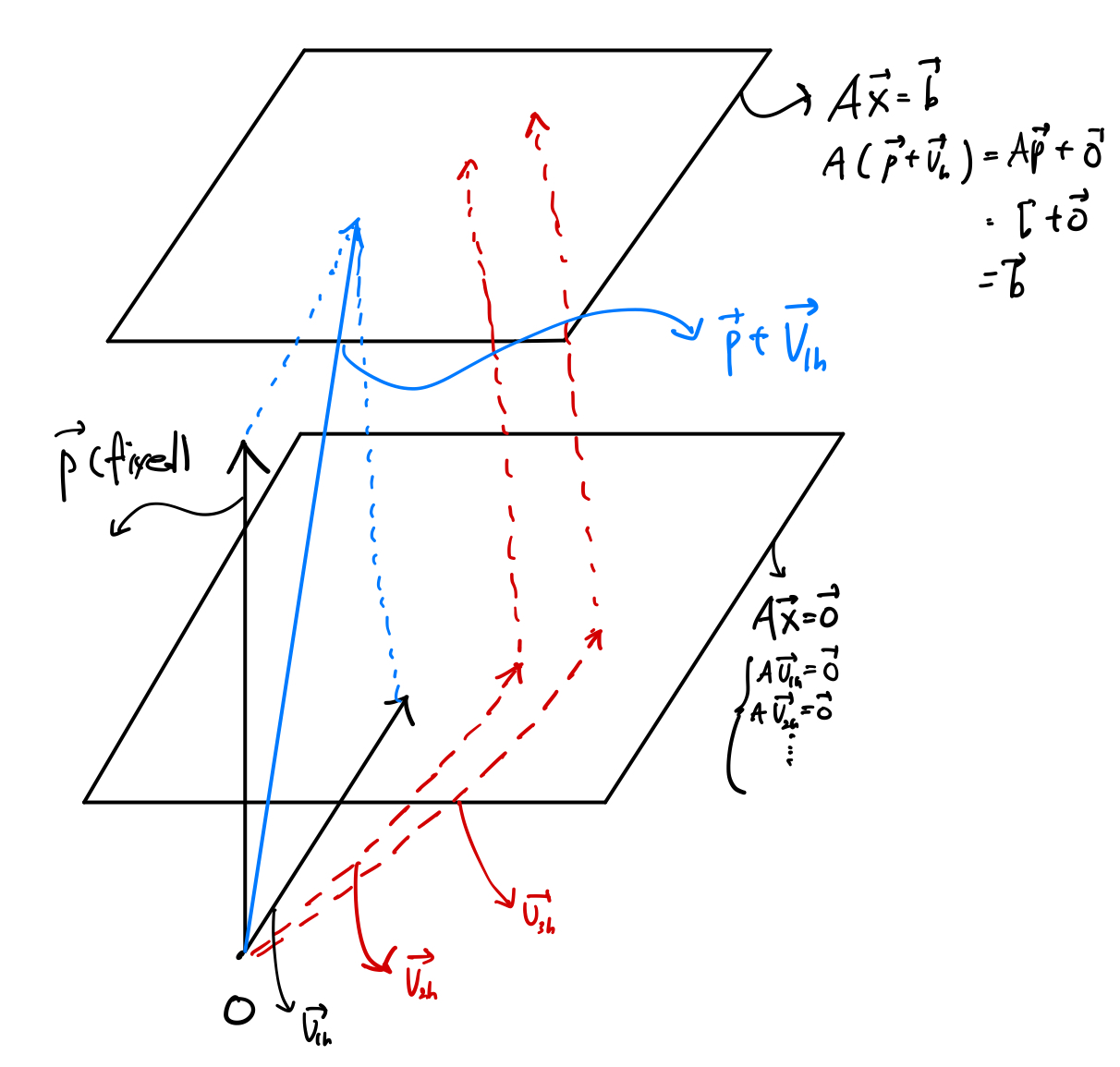
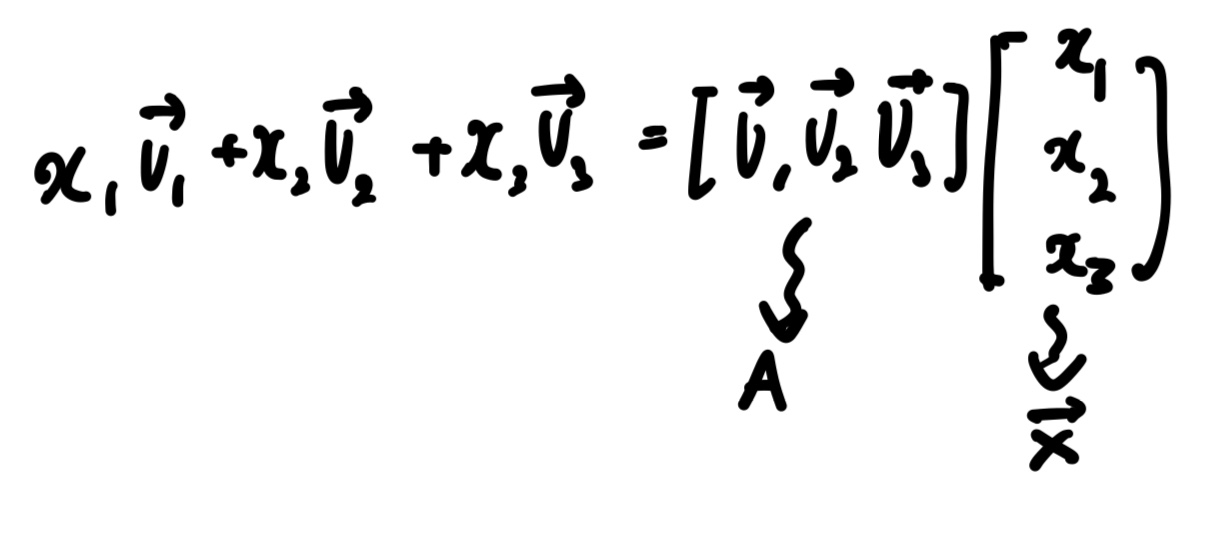이번 글에서는 Inverse matrix의 정의, 존재 조건, 성질, 역행렬 만드는 법을 정리했습니다. 목차 역행렬의 정의 역행렬의 존재 조건 역행렬의 성질 역행렬 만드는 법 1) Elementary Matrices 2) Gauss–Jordan Elimination 3) Adjoint & Determinant 역행렬과 연립방정식 머신러닝/딥러닝에서의 활용 역행렬의 정의 정방행렬 \(A \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times n}\)에 ..